5 Ways to Use AI in Virtual Care Without Sacrificing the Human Touch

AI is reshaping how virtual care is delivered across the United States. Even though health systems are adopting these new tools which improve accuracy, access, and efficiency, the focus needs to remain on the human relationship between patient and clinician which is still the foundation of great care.
People want convenience but they also want connection. Fast answers must come from people that they trust. AI, when used correctly, can help strengthen human connections. It can help clinicians listen more, engage more deeply, and spend time doing what they know how to do – treat their patients.
Below are five practical, evidence-backed ways healthcare organizations are using AI to enhance virtual care while keeping empathy front and center.
Why the Human Touch Still Matters in Virtual Care
Even in digital settings, empathy and trust influence outcomes. A study in Digital Health found that patients who feel heard and understood are more likely to follow care plans and report better overall experiences, even when interacting remotely.
At the same time, many patients worry that AI might replace the human parts of healthcare they value most. That’s why the most successful organizations focus on building human-centered AI, focusing on tools that support clinical teams rather than replace them.
1. Use AI to Strengthen Clinical Decision-Making
AI can help clinicians assess risk, catch early warning signs, and surface critical information faster. This support allows providers to spend less time hunting through data and more time with the patient.
Real-world examples:
- Mayo Clinic uses an AI-powered early warning system to flag patient deterioration sooner, improving response times without replacing clinicians.
- Cleveland Clinic has integrated AI into cardiology workflows, helping clinicians identify risks earlier and make more confident decisions.
- TytoCare uses AI to support remote lung sound analysis, improving quality and consistency during virtual exams.
Human impact:
Better insights mean richer conversations, clearer explanations, and more time focused on the person instead of the computer.
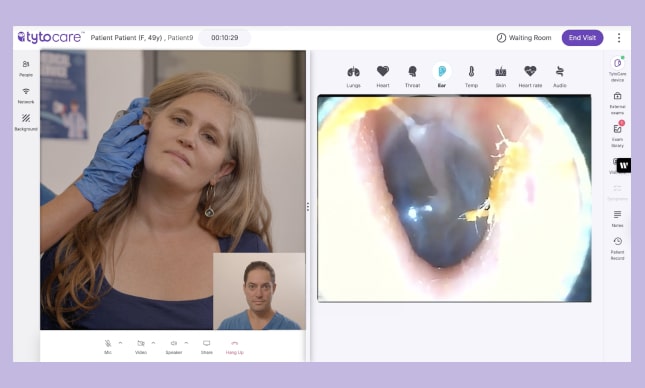
2. Use AI to Improve the Quality of Virtual Exams
One of the biggest challenges in virtual care is ensuring clinicians receive complete, accurate exam data. AI can guide patients or on-site staff step-by-step to capture the right images, sounds, and measurements.
Real-world examples:
- NYU Langone uses AI to assess the quality of patient-submitted dermatology images, reducing misdiagnosis risk and repeat visits.
- Children’s Mercy Kansas City uses AI-supported respiratory analysis tools to evaluate children’s breathing patterns.
- TytoCare applies AI guidance to help families and staff reposition devices during ear, throat, and lung exams so clinicians get the data they need.
Human impact:
Higher-quality exams lead to clearer care plans and more meaningful interactions so that follow-ups don’t feel rushed.
3. Use AI to Personalize Communication and Follow-Up
AI can tailor messages, next steps, and reminders based on a person’s health needs, behaviors, and risks. These tools help maintain continuity between visits without over-automating the experience.
Real-world examples:
- Kaiser Permanente uses AI to personalize preventive care reminders and follow-up pathways, improving patient engagement.
- Intermountain Health uses AI-enabled nudges to support medication adherence and chronic disease management.
Human impact:
Patients feel supported between visits, while clinicians stay focused on higher-value conversations.
4. Use AI to Reduce Administrative Burden So Clinicians Can Focus on People
Documentation, routing, coding, and intake can drain hours from a provider’s day. AI reduces this burden, helping clinicians reclaim valuable time.
Real-world examples:
- UCHealth uses ambient AI scribing to capture conversations automatically, eliminating manual note-taking.
- UCLA published a study that found AI scribes may reduce documentation time and improve physician well-being.
Human impact:
Less clicking. More connecting.
5. Use AI to Expand Access Without Replacing Providers
AI can bring high-quality care to more places like homes, rural clinics, urgent care centers, schools, and community sites, while keeping clinicians at the center.
Real-world examples:
- Ochsner Health uses AI to support remote hypertension programs, allowing clinical teams to oversee more patients with better outcomes.
- CVS MinuteClinics use AI triage to guide patients to virtual or in-person care, improving access in underserved regions.
- TytoCare brings guided remote exams into homes, schools, and community sites, helping providers expand reach without adding staffing strain.
Human impact:
More people receive timely care, and clinicians maintain control of decision-making.
Best Practices for Human-Centered, Ethical AI in Healthcare
Thoughtful AI requires strong guardrails. Leading organizations use established frameworks to ensure AI is safe, transparent, and always clinician-led.
Trusted guidance:
- World Health Organization guidelines on ethical AI in health
- American Medical Association principles for augmented intelligence
These reinforce a simple rule: AI should support clinical judgment, not override it.
Conclusion: AI Can Strengthen Human Connection If We Design It That Way
Healthcare has always been a human story. Whether care happens in a clinic, a school nurse’s office, or a family’s living room, people turn to people for reassurance and clarity. AI can help lighten the load by removing barriers and making virtual care smoother, but it’s the clinician who guides the conversation, reads the room, and brings comfort.
As virtual care continues to evolve, the goal isn’t to automate the human touch. It’s to protect it and to give clinical teams the tools they need to lead with confidence and compassion.